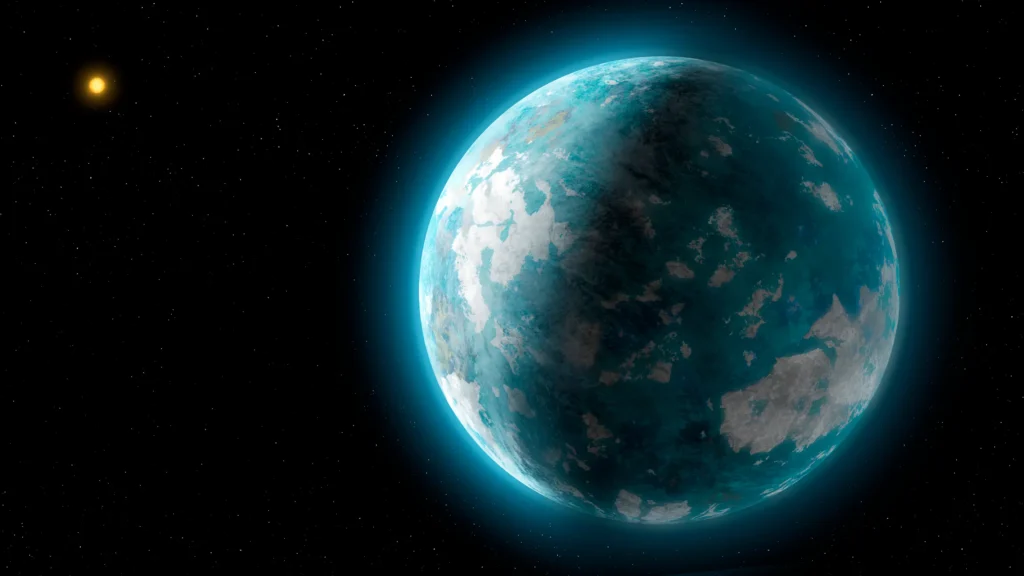

Astronomers have recently unveiled a stunning discovery just 19.7 light-years away—a super-Earth that exhibits one of the most extreme and intriguing orbits ever observed. Known as HD 20794d, this planet presents a unique case study in the quest for understanding celestial bodies that skirt the fringes of habitability. It sweeps in and out of its star’s habitable zone, hinting at the possibility of seasons that rival the fantastical tales of science fiction.
HD 20794d orbits a star slightly dimmer and less massive than our Sun, identified as HD 20794 or 82 Eridani, situated in the constellation Eridanus. The star shines brightly enough at magnitude 4.3 to be spotted without telescopic aid, making it a beacon in our night sky and a focal point for scientists probing the possibilities of life beyond Earth.

Eccentric Orbits and Extreme Climates
The planet’s orbit is a stark departure from the near-circular paths observed in our solar system. With an eccentricity measure of 0.4, HD 20794d’s path stretches from 0.75 astronomical units (AU) at its closest approach—nearer than Venus to our Sun—to a distant 2 AU, twice the Earth-Sun distance, at its farthest. This elongated orbit leads to drastic fluctuations in temperature, akin to having a winter that spans years followed by a brief, scorching summer.
“HD 20794d’s luminosity and proximity make it an ideal candidate for future telescopes whose mission will be to observe the atmospheres of exoplanets directly,” noted Xavier Dumusque of the University of Geneva, a leading member of the team that characterized this intriguing world.
The Challenge of Planetary Habitability
The varied distance of HD 20794d from its star poses significant questions about the conditions on its surface. At its furthest, the planet finds itself well outside the habitable zone, where temperatures plunge to potentially freeze any surface water. As it swings closer, it briefly traverses this life-sustaining region, warming up enough to perhaps allow liquid water before it retreats again into the cold.
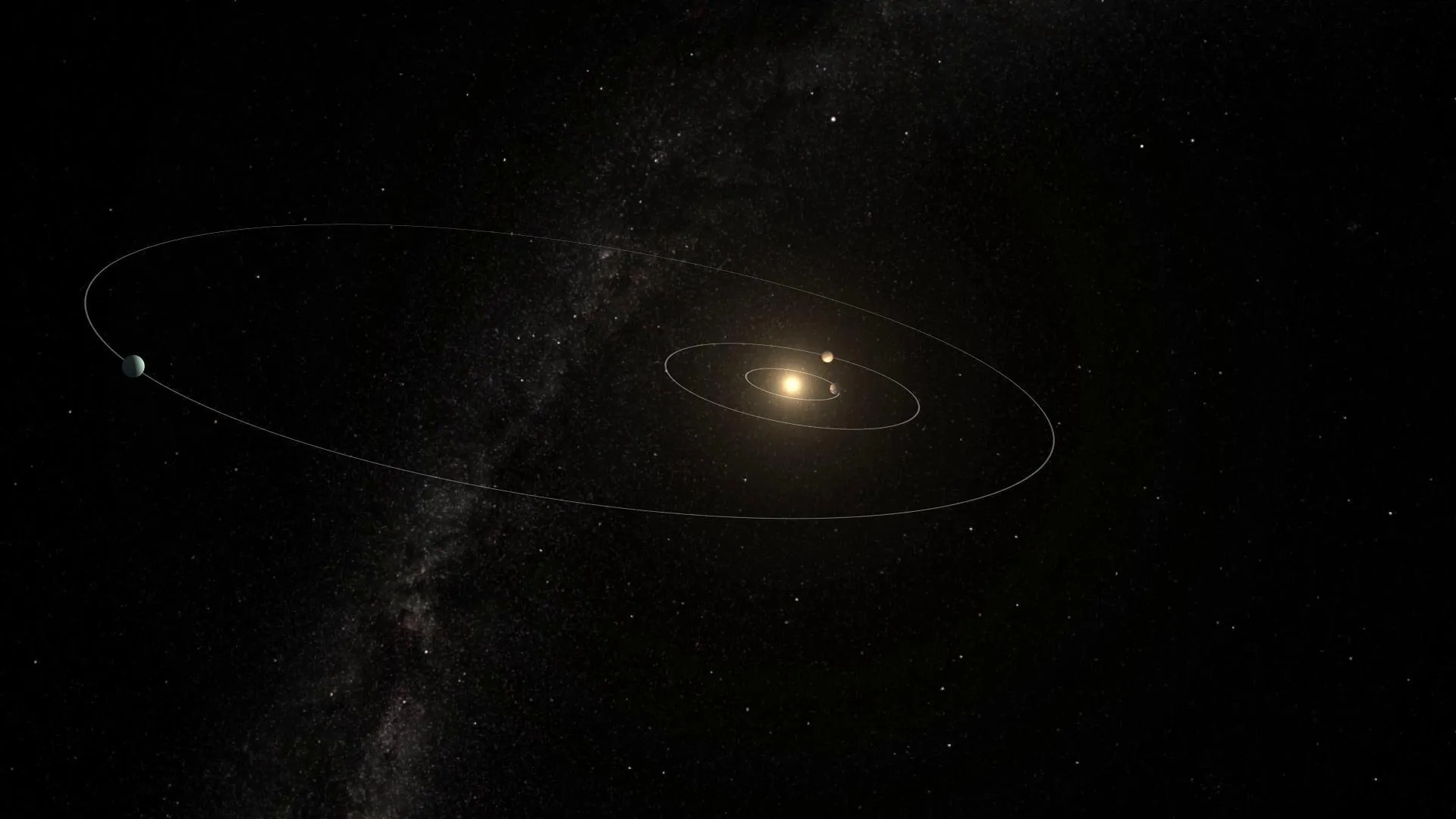
“Whether life could survive on such an extreme world is unknown,” admits Michael Cretignier from the University of Oxford. His team employed the YARARA algorithm to meticulously analyze data and confirm the planet’s existence amidst the background noise of cosmic signals.
The Imprint of a Chaotic Past
The peculiar orbit of HD 20794d suggests a tumultuous history marked by gravitational interactions with other planetary bodies. “The eccentricity of planets are remnants of planet–planet interactions during the early days of a planetary system,” explains Dumusque. This insight hints at a possible earlier configuration of the HD 20794 system, where another giant planet may have jostled HD 20794d into its current eccentric path before being ejected from the system entirely.

The Frontier of Exoplanet Research
HD 20794d’s discovery adds a critical piece to the puzzle of planetary formation and evolution. The planet’s extreme orbit provides a new perspective on the dynamic processes that govern planetary systems and challenges our understanding of what makes a planet suitable for life.
As we stand on the brink of a new era in astronomy, with next-generation telescopes poised to directly image the atmospheres of distant worlds, planets like HD 20794d offer a tantalizing glimpse into the vast diversity of the universe. The ongoing study of such worlds not only broadens our cosmic horizons but also deepens our appreciation of the delicate balance that makes Earth uniquely hospitable amidst the stars.
